Quantum computing is a devilishly advanced expertise, with many technical hurdles impacting its improvement. Of those challenges two vital points stand out: miniaturization and qubit high quality.
IBM has adopted the superconducting qubit street map of reaching a 1,121-qubit processor by 2023, resulting in the expectation that 1,000 qubits with in the present day’s qubit type issue is possible. Nonetheless, present approaches would require very giant chips (50 millimeters on a aspect, or bigger) on the scale of small wafers, or the usage of chiplets on multichip modules. Whereas this strategy will work, the intention is to achieve a greater path towards scalability.
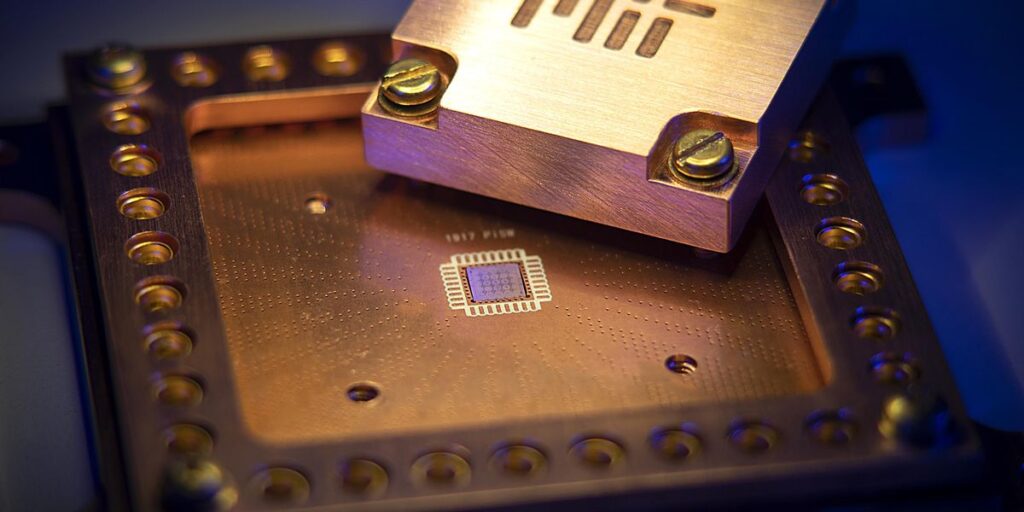
Now researchers at MIT have been able to both reduce the size of the qubits and carried out so in a means that reduces the interference that happens between neighboring qubits. The MIT researchers have elevated the variety of superconducting qubits that may be added onto a tool by an element of 100.
“We’re addressing each qubit miniaturization and high quality,” stated William Oliver, the director for the Center for Quantum Engineering at MIT. “Not like standard transistor scaling, the place solely the quantity actually issues, for qubits, giant numbers usually are not adequate, they need to even be high-performance. Sacrificing efficiency for qubit quantity just isn’t a helpful commerce in quantum computing. They have to go hand in hand.”
The important thing to this large improve in qubit density and discount of interference comes all the way down to the usage of two-dimensional supplies, particularly the 2D insulator hexagonal boron nitride (hBN). The MIT researchers demonstrated that just a few atomic monolayers of hBN may be stacked to type the insulator within the capacitors of a superconducting qubit.
Identical to different capacitors, the capacitors in these superconducting circuits take the type of a sandwich during which an insulator materials is sandwiched between two metallic plates. The large distinction for these capacitors is that the superconducting circuits can function solely at extraordinarily low temperatures—lower than 0.02 levels above absolute zero (-273.15 °C).
Superconducting qubits are measured at temperatures as little as 20 millikelvin in a dilution fridge.Nathan Fiske/MIT
In that surroundings, insulating supplies which might be accessible for the job, corresponding to PE-CVD silicon oxide or silicon nitride, have fairly just a few defects which might be too lossy for quantum computing functions. To get round these materials shortcomings, most superconducting circuits use what are referred to as coplanar capacitors. In these capacitors, the plates are positioned laterally to 1 one other, fairly than on prime of each other.
Consequently, the intrinsic silicon substrate under the plates and to a smaller diploma the vacuum above the plates function the capacitor dielectric. Intrinsic silicon is chemically pure and subsequently has few defects, and the big dimension dilutes the electrical subject on the plate interfaces, all of which results in a low-loss capacitor. The lateral dimension of every plate on this open-face design finally ends up being fairly giant (usually 100 by 100 micrometers) with a purpose to obtain the required capacitance.
In an effort to maneuver away from the big lateral configuration, the MIT researchers launched into a seek for an insulator that has only a few defects and is appropriate with superconducting capacitor plates.
“We selected to check hBN as a result of it’s the most generally used insulator in 2D materials analysis as a result of its cleanliness and chemical inertness,” stated colead creator Joel Wang, a analysis scientist within the Engineering Quantum Techniques group of the MIT Analysis Laboratory for Electronics.
On both aspect of the hBN, the MIT researchers used the 2D superconducting materials, niobium diselenide. One of many trickiest elements of fabricating the capacitors was working with the niobium diselenide, which oxidizes in seconds when uncovered to air, in accordance with Wang. This necessitates that the meeting of the capacitor happen in a glove field crammed with argon gasoline.
Whereas this may seemingly complicate the scaling up of the manufacturing of those capacitors, Wang doesn’t regard this as a limiting issue.
“What determines the standard issue of the capacitor are the 2 interfaces between the 2 supplies,” stated Wang. “As soon as the sandwich is made, the 2 interfaces are “sealed” and we don’t see any noticeable degradation over time when uncovered to the ambiance.”
This lack of degradation is as a result of round 90 p.c of the electrical subject is contained throughout the sandwich construction, so the oxidation of the outer floor of the niobium diselenide doesn’t play a major position anymore. This in the end makes the capacitor footprint a lot smaller, and it accounts for the discount in cross discuss between the neighboring qubits.
“The principle problem for scaling up the fabrication would be the wafer-scale development of hBN and 2D superconductors like [niobium diselenide], and the way one can do wafer-scale stacking of those movies,” added Wang.
Wang believes that this analysis has proven 2D hBN to be a very good insulator candidate for superconducting qubits. He says that the groundwork the MIT staff has carried out will function a street map for utilizing different hybrid 2D supplies to construct superconducting circuits.