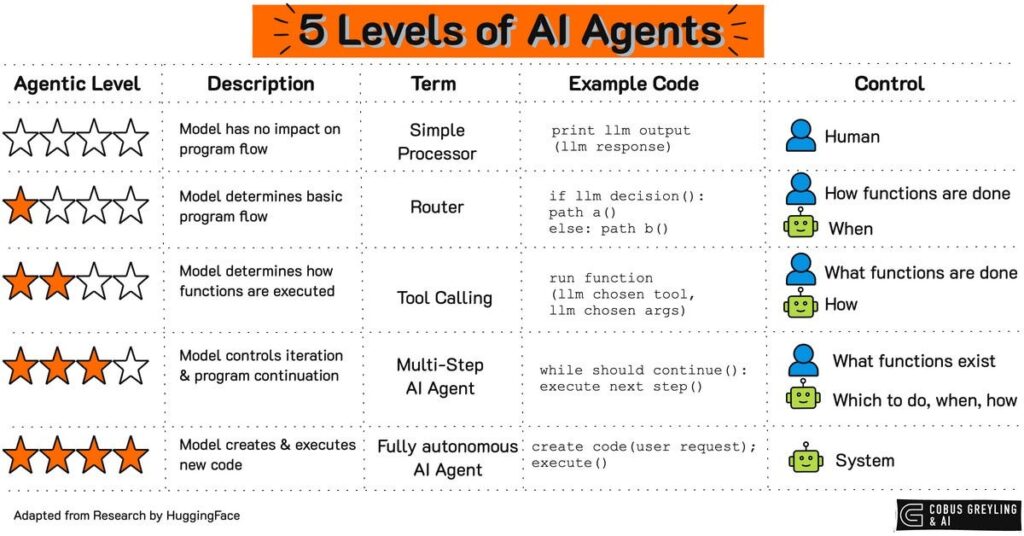
Ranges of AI Brokers are outlined as programs utilizing machine-learned fashions and may have totally different ranges of company.
They may also be mixed in multi-agent programs, the place one AI Agent workflow triggers one other, or a number of brokers work collectively towards a purpose.
The philosophical foundation for attributing company to AI stays unsure, elevating questions on whether or not AI can really possess it.
This has two key implications:
- The dangers related to increased ranges of company are usually not counterbalanced by a powerful philosophical justification for its advantages.
- As a substitute of debating whether or not AI possesses true company — an idea rooted in philosophy and sometimes related to intentionality, free will, and ethical accountability — it might be extra sensible to evaluate AI when it comes to autonomy.
Autonomy refers back to the means of an AI system to function independently inside predefined constraints, make choices primarily based on its programming and studying processes, and adapt to new inputs with out direct human intervention.
Wanting ahead, this means a number of essential instructions for the event of AI brokers:
Adoption of Agent Ranges
There needs to be widespread adoption of clear distinctions between ranges of agent autonomy. This may allow builders and customers to higher perceive system capabilities and the related dangers.
Human Management Mechanisms
It’s important to develop sturdy frameworks, each technical and policy-based, that guarantee significant human oversight whereas preserving useful semi-autonomous performance. This contains creating dependable override programs and establishing clear operational boundaries for AI Brokers.
Security Verification
New strategies have to be created to confirm that AI Brokers stay inside supposed working parameters and can’t override human-specified constraints.
The event of AI Brokers represents a essential inflection level in synthetic intelligence. Historical past has proven that even well-engineered autonomous programs could make catastrophic errors attributable to trivial causes.
Whereas elevated autonomy can present vital advantages in particular contexts, human judgment and contextual understanding stay indispensable, notably for high-stakes choices. Entry to the environments through which an AI agent operates is essential, empowering people to intervene and say “no” when a system’s autonomy diverges from human values and objectives.