Chipmaking giants like Intel, Samsung, and TSMC see a future the place key components of silicon transistors are changed with semiconductors which might be just a few atoms thick. Though they’ve reported progress towards that aim, that future is mostly considered more than a decade away. Now a startup spun out of MIT thinks it has cracked the code for making commercial-scale 2D semiconductors, and expects chipmakers to have built-in them in superior chips in half that point.
CDimension has developed a course of for rising molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), a 2D semiconductor, on silicon at a low-enough temperature that it’ll not harm underlying silicon circuits. That would enable the mixing of layers of 2D transistors above current silicon circuits and finally multi-tiered 3D chips made from 2D gadgets.
“Lots of people consider 2D semiconductors as one thing that’s nonetheless within the laboratory,” says CDimension CEO and co-founder Jiadi Zhu. “However CDimension has a proprietary device designed for 2D materials progress… and we’ve addressed lots of crucial [2D materials] problems concerning wafer-scale uniformity, concerning system efficiency and variation, concerning system reliability, and concerning compatibility with silicon manufacturing processes.” Taken collectively, 2D semiconductors are able to enter an industrial section of growth, he says.
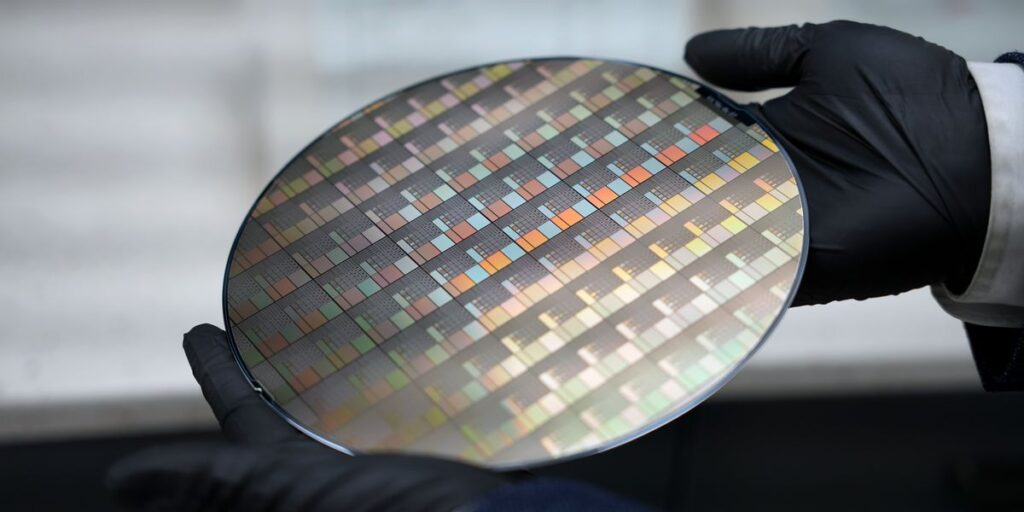
A lot of CDimension’s plans hinge on a proprietary course of that it makes use of to develop a single layer of MoS2 on silicon and different substrates at solely about 200 °C throughout complete 300 millimeter wafers. 2D supplies are shaped by chemical vapor deposition, whereby vaporized precursor chemical compounds react on a floor to coat it. However usually the reactions for making 2D supplies requires temperatures upwards of 1000 °C. That’s so excessive it will harm any underlying buildings wanted to make transistors. At present researchers get round that drawback by depositing the 2D semiconductor individually after which delicately transferring it to a silicon wafer. However CDimension’s system can develop the supplies proper on the silicon wafer with out harm.
The 2D Semiconductor Enterprise
A part of the startup’s enterprise proper now could be to ship silicon wafers with 2D materials grown on it so prospects can consider it and construct gadgets. Alternatively, prospects can ship wafers which have already been processed in order that they’ve silicon circuits or buildings on them. CDimension can then develop MoS2 or different 2D supplies atop that and ship it again to the shoppers, to allow them to combine a layer of 2D gadgets with their silicon circuits.
A check wafer made with CDimension’s course of sits beneath a microscope.CDimension
The latter could be 2D semiconductor’s first industrial entry. “We’re exhibiting the chances with silicon plus 2D materials,” Zhu says. “However 2D materials could be used for the highly-scaled logic gadgets as nicely. That may be the following step.”
Chipmakers like Intel, Samsung, and TSMC reported analysis aimed toward changing silicon nanosheets of their future transistors with MoS2 and different 2D semiconductors on the IEEE International Electron Device Meeting in December 2024. On the similar convention, Zhu and his colleagues from the MIT laboratories of IEEE Fellow Tomás Palacios and Jing Kong confirmed that the low-temperature synthesis could produce MoS2 transistors with a number of stacked channels, akin to nanosheet transistors. (Palacios is a strategic advisor to CDimension.) By cutting down the system, the workforce predicted that such gadgets might meet and exceed the necessities of the longer term 10A (1-nanometer) node by way of energy consumption, efficiency, and the realm they occupy.
An enormous motivation to go along with 2D semiconductors is to scale back energy consumption, says Zhu. Energy is misplaced in transistors each when they’re on (dynamic energy) and when they’re off (static energy). As a result of it’s simply over 0.6 nanometers thick, 2D transistors have qualities that might allow them to function utilizing about half the voltage of in the present day’s silicon gadgets, saving dynamic energy. When they’re off, it’s leakage current it’s important to fear most about. However MoS2 has a bandgap that’s greater than twice the worth of silicon’s, which means it takes way more power for cost to leak throughout the system. Zhu says gadgets made utilizing CDimension’s supplies consumed as little as one-thousandth the power of silicon gadgets.
Along with MoS2, which is an electron-conducting (n-type) semiconductor, the startup additionally supplies tungsten diselenide, a p-type semiconductor, in addition to 2D insulating movies, reminiscent of hexagonal boron nitride. The entire mixture can be wanted if 2D semiconductors are to ever take over in future CMOS chips.
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net